June 2023 — By Nate Shepherd, Suzi Airheart & Shaan Patel

The industrial recycling industry is undergoing rapid growth and transformation, shaped by various industry trends and M&A activity. At Harbor View, we have been closely monitoring the latest developments in the industrial recycling sector, including those with solar panels, e-waste, and light bulb recycling. We’ve also tracked various M&A drivers including increased acquisition spend, the integration of technology and innovation, private equity engagement, and consolidation strategies. Through our work with Complete Recycling Solutions in it’s acquisition by TerraCycle, we gained valuable firsthand insights into the dynamics of the recycling industry.
Solar Panels:
The management of end-of-life solar panels is in pressing need of improvement, as only 10% of solar panels in the U.S. are currently recycled (1). A contributing factor to this problem has been the lack of federal regulation regarding solar panel reuse and recycling. However, recent developments in state policies, business initiatives, and nonprofit solutions have been implemented with limited success.
To establish a more effective end-of-life solar panel process, two main approaches are being enacted. First, regulation to increase solar panel reuse has been implemented, encouraging panel owners to extend panel lifespans through repairs and refurbishing. Second, governments and manufacturers have begun collaborating to create a robust recycling system, which includes partnering with recycling vendors for more cost-effective alternatives to sending panels to landfills.
As policymakers engage in discussions regarding a more structured approach to solar panel recycling, service providers find themselves on the brink of an unexplored market opportunity.
E-waste:
The generation of electronic waste (e-waste) has been increasing rapidly, with estimates that over 347 million metric tons of e-waste exist globally (2). This includes various electronic devices such as smartphones, computers, televisions, and appliances, with some unaltered e-waste containing contaminants such as lead, chromium, cadmium, mercury, and other chemicals. Meanwhile, the current recycling rate for e-waste is alarmingly low, with less than 20% being recycled through proper channels (2).
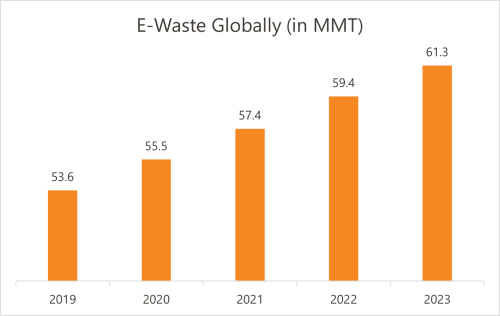
Sources: United Nations, Statista
Adopting a circular economy approach is crucial in tackling the e-waste problem. This approach involves designing products for durability, repairability, and recyclability. Most importantly, it entails establishing efficient collection and recycling systems while educating consumers about the importance of responsible disposal and recycling.
LED Bulbs:
Recycling LED light bulbs is largely beneficial as they contain valuable materials like glass, metals, and electronic components. By recycling these bulbs, users can conserve resources, reduce waste, and minimize environmental impact. It is essential to handle LED bulbs carefully during disposal due to the trace amounts of heavy metals including lead and arsenic contained in the bulbs’ microchips.
With LED technology being relatively new when compared to its counterparts, there has been a more proactive approach in planning how to dispose of LED products. Many communities have established recycling programs for LED light bulbs; local recycling centers, waste management facilities, and municipalities often accept them for recycling. Furthermore, certain retailers, such as home improvement stores or lighting retailers, offer in-store recycling programs for LED bulbs. Some LED bulb manufacturers have also implemented “take-back programs,” allowing consumers to return used bulbs directly to the manufacturer for proper recycling. Additionally, mail-in recycling services are available, which enable consumers to ship used LED bulbs to recycling facilities.
Industrial recycling service providers have the opportunity to capitalize on similar programs but will need to make investments in suitable equipment to effectively cater to the continuously expanding demand.
Growth in Acquisition Spend:
Major waste companies have significantly increased their acquisition spend, with an estimated $663 million spent on acquisitions in the first quarter of 2023 alone (3). This trend is expected to continue throughout the year. The investment in warehouse automation technology has proven fruitful for these companies, allowing them to compete with smaller firms, and subsequently acquire them, to fulfill customer service and collection system needs.
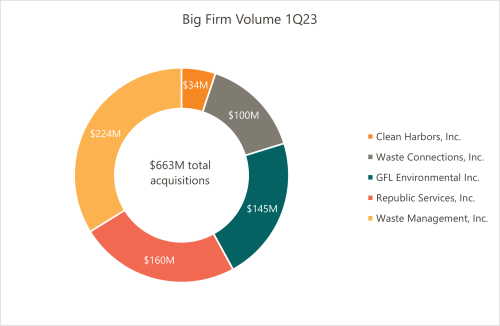
Source: PitchBook
Private Equity Involvement:
Private equity firms are actively investing in the waste and recycling industry, considering it an attractive investment opportunity that aligns with sustainability goals. These firms are fueling the growth of smaller players in the market and enabling them to compete on a larger scale. Private equity involvement brings increased funding to the sector, as well as opportunities for operational synergies and cost efficiencies.
Consolidation Strategies:
Both financial and strategic buyers in the industrial recycling industry are implementing consolidation strategies to strengthen their market positions and achieve economies of scale. These strategies include geographic expansion, where companies acquire regional recycling firms to expand their reach and gain access to new markets. By doing so, they can provide comprehensive waste management services to a broader customer base.
Another consolidation strategy involves portfolio diversification. Strategic buyers acquire companies offering complementary services, such as hazardous waste disposal or electronic waste recycling, to become one-stop solutions for various waste management needs. Integrating these services allows companies to offer comprehensive waste management solutions to clients.
Furthermore, some players in the industry are adopting vertical integration strategies. This is achieved by acquiring recycling facilities or waste-to-energy plants enabling them to control the entire value chain, from waste collection to recycling or energy generation. Vertical integration enhances operational efficiency and reduces dependency on external partners.
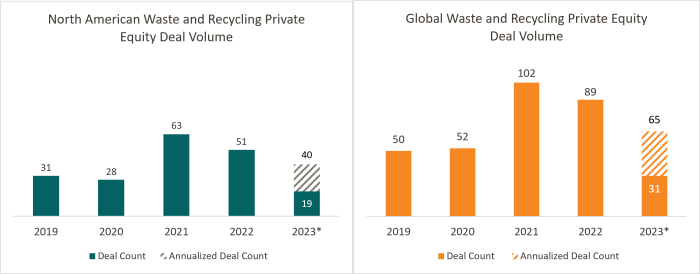
Source: PitchBook
Note: Transactions through 6/15/2023, shaded portion annualized and assumes performance continues at the same pace it has through 6/15/2023
Conclusion:
The industrial recycling industry is experiencing significant growth and transformation, driven by various industry trends and M&A activities. Solar panel, e-waste, and light bulb recycling are crucial areas of focus for creating a more sustainable future. By addressing the challenges in these areas and leveraging the opportunities they present, the industry can make substantial progress towards achieving a circular economy.
At Harbor View, we remain committed to monitoring and participating in the ongoing developments within the industrial recycling sector, helping selling founders achieve well deserved liquidity and buyers attain company growth through strategic acquisition.
Sources:
DISCLAIMER This presentation is intended for information and discussion purposes only and does not constitute legal or professional investment advice. Statements of fact and opinions expressed are those of the participants individually and, unless expressly stated to the contrary, are not the opinion or position of Harbor View Advisors, LLC (“HVA”). The information in this presentation was compiled from sources believed to be reliable for informational purposes only. HVA does not endorse or approve, and assumes no responsibility for, the content, accuracy or completeness of the information presented.